Copper in 2026 has quietly evolved from a background industrial material into one of the world’s most vital resources. It powers everything: renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, data centres, urban infrastructure, and advanced defence technologies. The growing phrase “Copper is the new gold” perfectly captures this global transformation.
Unlike gold, which holds symbolic and financial value, copper’s true strength lies in its functionality. It serves as the hidden engine of progress, ensuring that modern systems continue to operate efficiently. Every electrical circuit, data connection, and clean energy charging point relies on copper’s exceptional conductivity and durability.
As industries accelerate toward cleaner, smarter, and more connected economies, copper in 2026 stands at the center of it all. The century’s economic and technological growth now depends on how effectively nations manage, produce, and recycle copper marking not just a market shift but a defining phase in global industrial evolution.

Copper Ore: The Beginning of a New Industrial Cycle
Understanding Copper Ore and Its Importance
Copper ore is the raw mineral extracted from the earth to produce refined copper. Found in both oxide and sulphide forms, these ores are processed through complex refining methods to produce pure copper metal used across industries.
The importance of copper ore has increased dramatically as demand expands in manufacturing, energy, construction, and electronics. The metal extracted from it plays an essential role in shaping the global economy through its use in:
- Power Infrastructure Development: Copper forms the foundation of global power grids, transmission lines, and substations that drive industrial and residential electricity access.
- Construction and Plumbing Systems: Modern cities rely on copper for water pipelines, building wiring, and HVAC systems, ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity.
- Renewable Energy Expansion: Solar, wind, and battery energy systems require high-purity copper wiring to ensure efficient energy transfer and storage stability.
- Electric Vehicle Manufacturing: EVs depend on copper for motors, inverters, batteries, and charging equipment that support the clean transport revolution.
- Defence and Communication Technology: From radar systems to semiconductors, copper enables national defence networks and advanced electronic systems.
Copper-producing countries like Chile, Peru, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the United States dominate the supply chain, making them central players in the global resource economy.
Global Copper Demand in 2026
The Expanding Role of Copper in the Modern Economy
Copper is now the most essential industrial metal after iron and aluminium. Its global demand is projected to exceed 30 million metric tonnes in 2026, reflecting a major leap in usage across multiple industries. This surge is driven by the push toward electrification, renewable energy adoption, and digital connectivity.
Copper is not just a construction material; it is the metal that sustains progress. It powers the infrastructure that supports economic growth and technological evolution. The modern economy’s most transformative sectors rely heavily on copper:
- Clean Energy Infrastructure: Renewable grids, wind farms, and solar systems all depend on copper for wiring and efficient power transmission.
- Urban Development: Smart cities use copper-based systems for transport electrification, building automation, and water supply.
- Data and AI Systems: Every data centre and AI-driven facility requires copper cables to ensure consistent and stable power flow.
- Global Trade and Industry: Manufacturing hubs in Asia, Europe, and the Americas depend on copper imports for industrial production.
As the world transitions to greener technologies, copper’s demand is expected to continue rising steeply through the decade.
You can read here to learn more about “Copper Price Outlook : Is Copper Becoming a Top Investment?“
Technology and Infrastructure: Building the Future with Copper

Copper’s Expanding Role in Modernisation
Technological development and copper are now inseparable. Every modern innovation, from renewable power to digital networks, depends on it. Its versatility makes it indispensable across multiple sectors.
Key factors driving technological dependence on copper include:
- Electrification of Transportation: The global shift toward electric vehicles requires high volumes of copper wiring and charging infrastructure. Each EV contains up to 80 kilograms of copper across motors, batteries, and power systems.
- Expansion of Smart Cities: Urban electrification projects depend on copper for building automation, lighting, and public transit energy systems.
- 5G and Data Connectivity: As 5G networks expand globally, copper ensures reliable and stable data transmission in both urban and rural areas.
- Renewable Power Integration: Solar farms, wind installations, and battery storage all rely on copper’s conductivity to efficiently channel and distribute energy.
- Digital Industrialisation: Automated manufacturing, robotics, and AI-driven production require copper components for precision, safety, and durability.
Copper has become the bridge connecting traditional industry with the digital economy. Its role in both physical and virtual infrastructure cements its status as a true driver of modernisation.
Copper in the Electric Vehicle Revolution
How EVs are Changing Copper Demand
The global transportation sector is undergoing a complete transformation. Electric vehicles have become the symbol of sustainable progress, and copper is the foundation behind this shift.
Electric vehicles use significantly more copper than traditional combustion-engine vehicles. The increase comes from multiple areas:
- Motors and Battery Systems: Electric drivetrains require high-purity copper wiring to ensure efficient power delivery and energy storage.
- Charging Infrastructure: Rapid expansion of public and private charging stations across continents depends heavily on copper cables and transformers.
- Thermal Management and Safety: Copper’s excellent thermal conductivity helps manage heat in high-voltage systems, enhancing safety and performance.
- Manufacturing Equipment: Copper-based machinery and tools are used in EV assembly and battery production lines worldwide.
The rise in EV production and adoption means copper demand from the transport sector will continue to soar through 2030, reshaping trade routes and resource policies globally.
Copper in Renewable Energy Systems
The Backbone of Clean Energy Infrastructure
The renewable energy revolution is built on copper. Whether it’s the sun, wind, or water, each renewable energy source depends on copper’s electrical efficiency.
Copper is used extensively in:
- Solar Power Systems: Photovoltaic cells rely on copper connections for stable and efficient energy flow. Every large-scale solar farm uses thousands of tonnes of copper wiring.
- Wind Turbines: Each modern wind turbine contains between 4 and 8 tonnes of copper, used in generators, grounding systems, and transmission components.
- Battery and Grid Storage: Energy storage networks depend on copper for consistent performance and longevity, enabling smooth energy transition during peak demand.
- Smart Energy Distribution: Copper-based smart grids ensure optimised energy delivery and monitor consumption in real time, reducing energy loss.
The global goal to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 is impossible without copper. It is the hidden force connecting renewable energy production, transmission, and distribution.
Sustainable Mining: The Path to Responsible Growth
Reinventing Copper Extraction for a Greener Future
As copper demand reaches new heights, the environmental impact of mining has become a global concern. The focus is now on sustainable mining practices that balance production efficiency with environmental protection.
Long-term solutions and technological innovations driving sustainable mining include:
- Water Conservation and Recycling: Modern facilities are implementing closed-loop systems that recycle mining water and prevent contamination of surrounding ecosystems.
- Smart Exploration Technologies: AI and digital mapping tools help identify rich ore deposits with minimal land disruption.
- Efficient Processing Techniques: New refining technologies allow for better recovery of copper from lower-grade ores, reducing waste and emissions.
- E-waste and Scrap Recycling: Increasing use of recycled copper from electronic waste and decommissioned infrastructure reduces dependence on fresh extraction.
- Emission Monitoring and Carbon Neutrality Goals: Companies are investing in carbon tracking systems and renewable-powered operations to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
This evolution marks a shift from traditional extraction to responsible, intelligent, and eco-efficient mining practices that align with global sustainability targets.
Geopolitical Significance: Copper as a Strategic Resource
How Control of Copper Shapes Global Power
Copper has quietly become a pillar of geopolitical strength. The nations that control its production and supply chains now hold strategic leverage in trade and technology.
- Chile: The world’s leading copper producer, providing nearly a third of the global supply and maintaining massive untapped reserves.
- Peru: A rapidly expanding producer, backed by international investments and infrastructure development.
- Democratic Republic of Congo: Holds vast reserves of copper and cobalt, essential for EV batteries and renewable technologies.
- United States: Increasing domestic mining projects to strengthen supply security and reduce foreign dependence.
Global trade now hinges on copper availability. It has replaced oil as the new strategic resource that influences national policies, trade routes, and industrial strategies.
Copper Beyond Industry: Defence, Health, and Innovation
A Metal That Powers Multiple Sectors
Copper’s role now stretches far beyond energy and manufacturing. In 2026, it has become indispensable to defence, healthcare, and advanced technology. Its combination of electrical conductivity, heat resistance, and antimicrobial properties makes it essential across industries that demand reliability and safety.
From powering AI systems to protecting soldiers and patients, copper serves as both a technological and humanitarian asset.
Defence Electronics and Aerospace Systems
Copper ensures precision and stability in defence communication, radar, and satellite systems. It supports high-frequency signal transmission, power regulation, and electromagnetic shielding.
- Military and Radar Systems: Copper wiring delivers consistent performance under extreme heat and high voltage.
- Aerospace Engineering: Copper alloys are used in propulsion systems, electrical grounding, and heat shields for spacecraft and aircraft.
- Strategic Reliability: Its durability ensures uninterrupted defence communication and navigation across multiple terrains.
Public Health and Antimicrobial Applications
In healthcare, copper’s natural ability to destroy bacteria and viruses has transformed how hospitals and public spaces are designed.
- Hospital Surfaces: Operating rooms and ICUs use copper fixtures to prevent microbial growth.
- Public Infrastructure: Transport systems, elevators, and air filters now include copper components to maintain hygiene in high-contact zones.
- Clean-Air Technology: Copper-based HVAC systems neutralise airborne contaminants, improving air quality in smart cities.
These applications make copper a silent yet powerful ally in protecting public health.
Digital Devices, Semiconductors, and AI Hardware
Every semiconductor, circuit, and microchip depends on copper’s conductivity to function efficiently.
- AI Servers and Processors: Copper wiring supports stable, high-speed data transfer in computing systems.
- Telecommunication Networks: 5G towers and routers use copper to minimise resistance and power loss.
- Quantum and Edge Computing: Advanced chips rely on copper layers to handle complex processing loads safely.
Copper’s reliability ensures the backbone of modern digital technology remains strong.
Why Copper’s Versatility Matters
Copper’s presence in defence, medicine, and digital infrastructure highlights its unmatched versatility. It is the only metal combining strength, conductivity, antimicrobial safety, and economic value, making it the most strategic industrial material of the modern age.
Copper Recycling and the Circular Economy
Closing the Loop for Sustainable Growth
Recycling is now a cornerstone of the global copper supply chain. Unlike other metals, copper retains full conductivity and strength even after repeated recycling. This makes it central to the circular economy, where materials are reused instead of mined anew.
Recycling ensures a continuous supply of copper while supporting energy efficiency and environmental protection.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection
Recycling copper uses nearly 85% less energy than mining new ore, making it both cost-effective and eco-friendly.
- Reduced Emissions: Lower energy use directly cuts greenhouse gas output.
- Cleaner Operations: Recycling avoids landscape disruption and water contamination caused by traditional mining.
- Conservation: Reuse of existing copper reserves reduces strain on natural resources.
Recycling transforms copper from a mined commodity into a renewable industrial asset.
Economic Value and Industrial Benefits
The secondary copper market contributes billions annually to global GDP and supports sustainable job creation.
- Employment Opportunities: Recycling facilities generate steady green jobs in collection and processing.
- Revenue Streams: Reclaimed copper from vehicles, cables, and electronics becomes a profitable raw material.
- Industrial Stability: Domestic recycling reduces dependence on imports and price volatility.
Recycling strengthens both national economies and long-term supply security.
Circular Economy Models and Future Outlook
Modern industries now integrate recovery systems into production cycles, ensuring continuous material use.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Factories reuse copper waste directly in new production.
- Renewable Integration: Recycled copper powers EVs, grids, and storage systems sustainably.
- Policy Support: Governments offer tax benefits and incentives for industries using recycled materials.
This shift from extraction to regeneration ensures that copper remains a sustainable pillar of the global economy.
Recycling as a Strategic Necessity
Recycling copper is now recognised as a strategic safeguard for energy security, economic stability, and environmental preservation. It closes the resource loop and defines the future of sustainable industrial progress.
Market Outlook: Copper Prices and Future Demand
Tightening Supply Meets Rising Global Need
Between 2023 and 2026, copper has shown remarkable stability despite market volatility. The combination of surging demand and limited new supply has created a consistent upward pressure on prices.
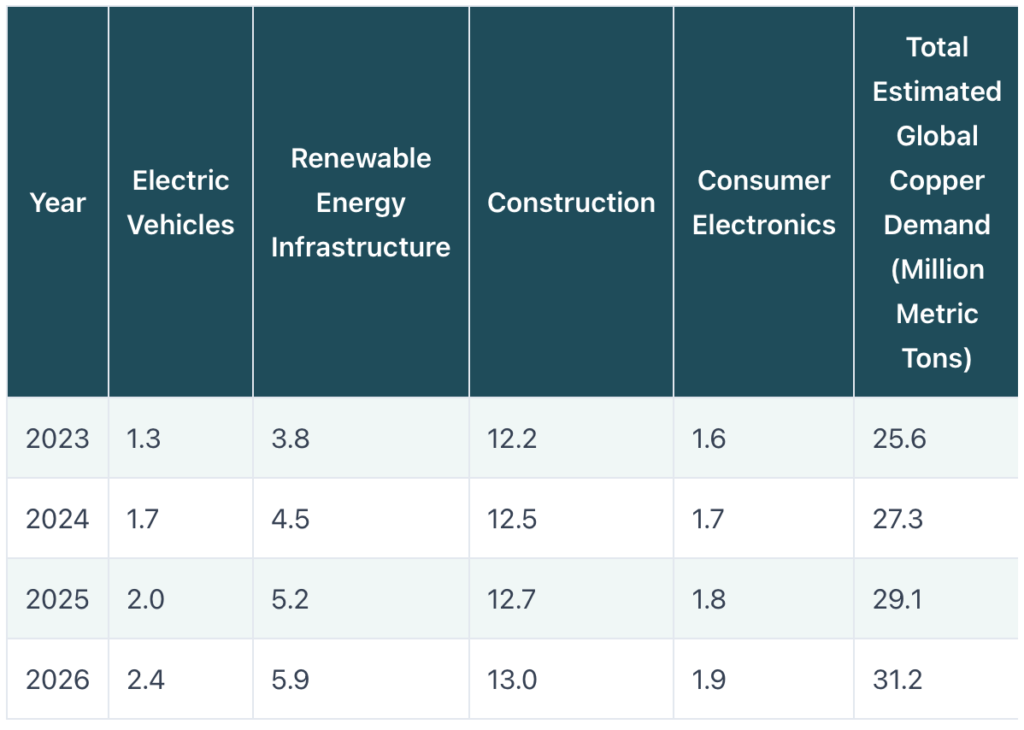
Analysts project that the global copper market will face a deficit exceeding 5 million metric tonnes by 2027, primarily due to the rapid growth in renewable energy and EV sectors.
For traders and investors, this means:
- Steady Price Appreciation: As supply lags behind consumption, copper prices are expected to maintain an upward trajectory.
- Rising Investment Opportunities: Green mining, recycling, and clean technology sectors are attracting heavy capital inflows.
- Strategic Stockpiling: Governments and corporations are securing copper inventories to hedge against future shortages.
- Long-Term Growth Outlook: Copper remains one of the few commodities offering both stability and consistent value appreciation in the coming decade.
Global Minerals Outlook: The Broader Picture
Copper’s story is part of a wider shift toward critical minerals shaping global energy and technology systems. Alongside copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements are essential to the renewable revolution.
Between 2022 and 2024, solar generation and battery storage capacity more than doubled, driving rapid expansion in mining, recycling, and material recovery technologies. Artificial intelligence, digital twins, and blockchain are making mineral extraction and trade more transparent, efficient, and ethical.
The future will belong to nations that treat mineral resources not just as commodities, but as strategic pillars of innovation and environmental balance.
You can read here to learn more about Top Metals in 2026 Reshaping Industries and Investment Trends
A Call to Action for Sustainable Growth
The world stands at a critical moment where industrial growth and environmental responsibility must move together. Governments, industries, and investors have a shared duty to ensure that copper and all critical minerals are extracted, managed, and recycled responsibly.
Sustainable growth depends on:
- Adoption of green mining and low-carbon technologies across major production hubs.
- Creation of circular economy models that minimise waste and maximise resource recovery.
- Strong global collaboration for transparent and ethical trade in critical resources.
- Encouragement of investment in recycling, AI-driven exploration, and renewable-powered mining.
Those who adapt early to these changes will lead the next generation of sustainable industrialisation.
Key Takeaways
- Copper has become the new gold of the 21st century, essential for energy, technology, and infrastructure.
- Global copper demand in 2026 exceeds 30 million metric tonnes, fuelled by electric vehicles and renewable energy.
- Sustainable mining, recycling, and circular economy practices are transforming the copper industry.
- Control of copper supply grants nations strategic economic and political influence.
- Technological advancements such as AI and digital monitoring are reshaping how copper is sourced and processed.
- For investors, copper remains a reliable long-term asset tied directly to global progress.
Read here to learn more about “7 Reasons Gold and Silver Market Remains Strong 2026“
Source of image : google

I’m Chaitali Sethi, a financial writer and market strategist focused on Forex trading, market behaviour, and trader psychology. I simplify complex market movements into clear, practical insights that help traders make better decisions and build a stronger trading mindset.